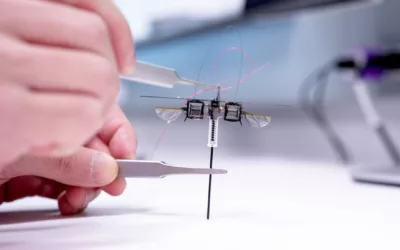
Researchers from the Harbin Institute of Technology (HIT) in China have developed a microscopic robot that can travel through blood vessels and precisely deliver drugs to targeted areas in the body. The design of the micro-robot is inspired by human cells and the tiny tardigrade creature, which is known as the most durable animal on Earth. The robot’s shell has three layers, including an inner magnetic layer that generates power, a middle gel layer that provides connectivity, and an outer camouflage membrane that resembles a human cell, offering biocompatibility and reducing friction. The clawed structure on the robot’s surface was inspired by the microscopic tardigrade, and it enables movement along the interior of blood vessels with minimal pressure.
One of the major challenges in creating micro-robots is making them move against the flow of blood in veins, but the team has developed a solution by using an external rotating magnetic field to control the robot’s motion. The robot moves along blood vessels with a rolling motion, similar to a wheel, and can securely attach itself to desired tissues using its claw-like structure. The surface of the robot employs a structure that mimics red blood cells, which enhances biocompatibility and reduces resistance. The team uses real-time intravascular optical coherence tomography (IVOCT) to guide and track the robot’s position within blood vessels.
The micro-robot’s development paves the way for future applications where the robot could deliver drugs directly to targeted areas in the body, potentially improving drug efficiency while reducing dosage and side effects. Currently, chemotherapeutic drugs for cancer treatment are delivered through intravenous injection, with only about 0.07% of the drug reaching the targeted area. The use of these micro-robots could improve drug delivery by achieving efficient navigation and retention within veins, allowing the drug to be retained in the targeted area. Overall, this development represents a significant step forward in the field of medical technology, offering new possibilities for targeted drug delivery and improved treatment outcomes.