A Brief History of Robots
The history of robots is a fascinating tale that stretches back thousands of years. The word “robot” comes from the Czech word “robota,” which means “forced labor.” Throughout history, people have been fascinated with the idea of creating machines that can perform tasks automatically, without human intervention.
Ancient Robots
 The ancient Greeks and Egyptians were among the first to create machines that could perform tasks automatically. Greek mathematician Archytas created a wooden pigeon that could fly, while the Egyptian god Thoth was said to have created a statue that could speak.
The ancient Greeks and Egyptians were among the first to create machines that could perform tasks automatically. Greek mathematician Archytas created a wooden pigeon that could fly, while the Egyptian god Thoth was said to have created a statue that could speak.
In China, the invention of clockwork mechanisms in the 3rd century BCE allowed for the creation of complex automata. The Chinese also developed mechanical puppets for use in religious ceremonies.
Medieval Robots
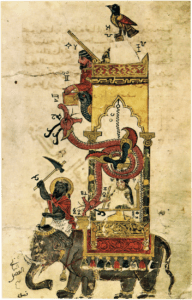 During the Middle Ages, European inventors created automata that could perform a variety of tasks. In the 13th century, Al-Jazari, an inventor from the Islamic world, created a number of automata, including a boat that could row itself and a musical automaton that played the flute.
During the Middle Ages, European inventors created automata that could perform a variety of tasks. In the 13th century, Al-Jazari, an inventor from the Islamic world, created a number of automata, including a boat that could row itself and a musical automaton that played the flute.
In the 15th century, Leonardo da Vinci designed a number of automata, including a mechanical lion that could walk and move its head and tail.
Industrial Revolution

Joseph-Marie Jacquard in 1801
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries brought about a new era of automation. Machines were developed to perform a variety of tasks, including weaving, spinning, and milling. These machines were the precursors to modern robots.
The first programmable machine was created by French inventor Joseph-Marie Jacquard in 1801. Jacquard’s loom used punched
cards to control the weaving process, and it could produce complex patterns automatically.
Modern Robotics
 The modern era of robotics began in the mid-20th century. In 1954, George Devol and Joseph Engelberger created the first industrial robot, the Unimate, which was used in a General Motors plant to perform repetitive tasks.
The modern era of robotics began in the mid-20th century. In 1954, George Devol and Joseph Engelberger created the first industrial robot, the Unimate, which was used in a General Motors plant to perform repetitive tasks.
In the 1960s and 1970s, research in robotics expanded, and robots were developed for a variety of applications, including space exploration, manufacturing, and medicine.
In the 1990s, robots became more sophisticated and began to be used in new areas, such as entertainment and education. The Sony AIBO, a robotic dog, was introduced in 1999 and became a popular consumer product.
Today, robots are used in a wide range of industries and applications, from manufacturing and logistics to healthcare and agriculture. They are becoming more advanced and capable, with new developments in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and computer vision.
In conclusion, the history of robots spans thousands of years and has been shaped by the ingenuity of inventors and the needs of society. From ancient automata to modern-day robots, these machines have helped us perform tasks more efficiently and effectively, and they will continue to play an important role in our lives in the years to come.